China’s Shenzhen Salubris Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd (SHE: 002294) announced that the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has accepted a clinical filing for its novel gene editing drug YOLT-101, licensed from YolTech Therapeutics. This PCSK9-targeted base editing drug is intended for the treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), marking a significant step forward in the development of innovative therapies for inherited lipid disorders.
Drug Mechanism and Technology
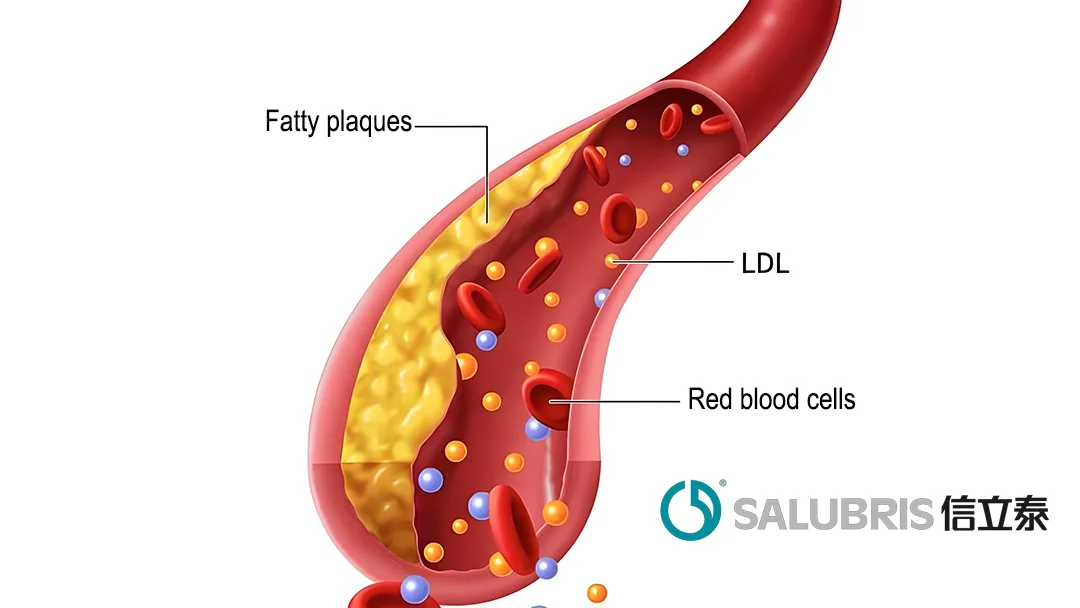
YOLT-101 comprises YolBE (a base editor) and guide RNA (gRNA) encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). The LNPs facilitate liver targeting, enabling the drug to be internalized into liver cells via the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR). Once inside, the base editor and gRNA form a complex that targets specific sequences of the PCSK9 gene. By inducing base editing at specific sites, the drug shuts down PCSK9 gene expression. This mechanism inhibits PCSK9-mediated degradation of LDLR, increases LDLR binding to low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and effectively reduces LDL-C levels in the blood.
Collaboration and Development
Salubris Pharmaceuticals secured the rights to YOLT-101 through a licensing agreement with YolTech Therapeutics in August of the previous year. The acceptance of the clinical filing by the NMPA represents a critical milestone in bringing this innovative gene editing therapy closer to patients with familial hypercholesterolemia.-Fineline Info & Tech